🐍What is Python?
Python is a Open source, general purpose, high level, and object-oriented programming language. It was created by Guido van Rossum. Python consists of vast libraries and various frameworks like Django, Flask, Pandas, CherryPy, and Web2Py etc.
👨💻How to Install Python in Linux?
You can install Python in all operating system like Linux, Ubuntu, Windows & MacOS.
Installation of Python in Linux:
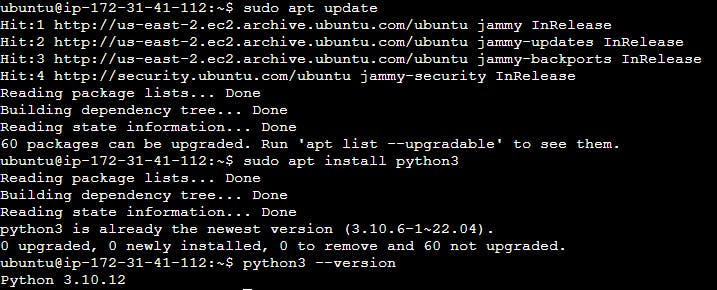
Update the package index: It's a good practice to update the package index before installing any new packages:
sudo apt update #For Ubuntu/ DebianInstall Python: You can install Python using the package manager:
sudo apt install python3 #For Ubuntu/Debian sudo yum install python3 #For CentOS/RHELVerify the Installation: After installation, you can verify that Python was installed successfully by running:
python3 --version
👨💻Task: Installation of Python in Linux with Example.
👨💻Different Data Types in Python
In Python, there are several built-in data types that are used to store different kinds of data. Here are some of the most commonly used data types along with examples:
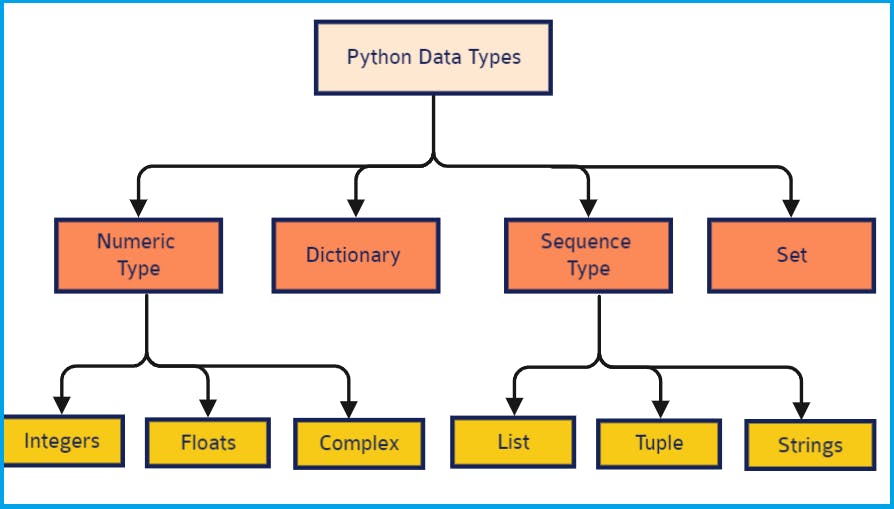
Integer (
int): Represents whole numbers without any fractional part.x = 10 y = -5Float (
float): Represents real numbers with a decimal point.pi = 3.14 temp = -20.5String (
str): Represents a sequence of characters enclosed within single quotes (') or double quotes (").name = 'Patrik' msg = "Hello, Python Learners!"Boolean (
bool): Represents either True or False.a = True b = FalseList (
list): Represents an ordered collection of items. Items can be of different data types.numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] fruits = ['Kiwi', 'Banana', 'Jackfruit']Tuple (
tuple): Similar to lists, but immutable (cannot be changed once created).thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")Dictionary (
dict): Represents a collection of key-value pairs. Keys are unique within a dictionary.person = {'name': 'Patrik', 'age': 23, 'city': 'New Nashik'}Set (
set): Represents an unordered collection of unique items. Duplicates are not allowed.unique_numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} vowels = {'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'}NoneType (
None): Represents the absence of a value or a null value.COPY
result = None
💥Conclusion:
In conclusion, Python is a versatile and powerful programming language known for its simplicity and readability. Its rich set of built-in data types, control structures, and extensive standard library make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from web development and data analysis to artificial intelligence and DevOps.
👨💻
