📑Let's Docker Build and Run Knowledge
docker build - Building Docker Images.
In the context of our pipeline, it's like creating a blueprint for your application and packaging it into a standalone image.
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'docker build -t mandgepratik/django-app:latest .'
}
}
}
docker run - Run Docker Container.
In our pipeline, it's like deploying your application in an isolated environment.
stages {
stage('Run') {
steps {
sh 'docker run -d mandgepratik/django-app:latest'
}
}
}
Now Let's tackle our tasks,
📑Task 1: Create a Docker-Integrated Jenkins Declarative Pipeline.

📍For Jenkins Installation You need to Install Java.
sudo apt update #update system
sudo apt install fontconfig openjdk-17-jre #Java Installation
📍Then, Install Jenkins, Docker & Docker-compose.
# Full Installation of Jenkins
sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
-----------------------------------------------------------
# Full Installation Of Docker & Docker-Compose
sudo apt-get install docker.io docker-compose -y
📍Enable Jenkins & Docker
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
sudo systemctl enable docker
📍Then, Add Users in docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER #ubuntu user
sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins #Jenkins user
cat /etc/group # check both user add or not
📍Go to security group, open port 8080 for Jenkins & 8000 for Docker.

📍Then Access Jenkins Portal using your EC2 public-ip:8080
📍Now, creating new pipeline job. Go to New Item->Give name of Project->select Pipeline->Click OK.
📍Go to pipeline, Configure you pipeline.
📍Go to last, select Pipeline script-> write this script-> Save it.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage("code") {
steps {
git url: "https://github.com/mandgepratik/node-todo-cicd.git", branch: "master"
echo "code cloned successfully"
}
}
stage("build") {
steps {
sh 'docker build . -t todo-app'
echo "code build successfully"
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
sh "docker run -p 8000:8000 -d todo-app"
echo "Node-app deployed successfully"
}
}
}
}
📍On the Left, Click on Build Now.
📍On First Click your Pipeline runs successfully.
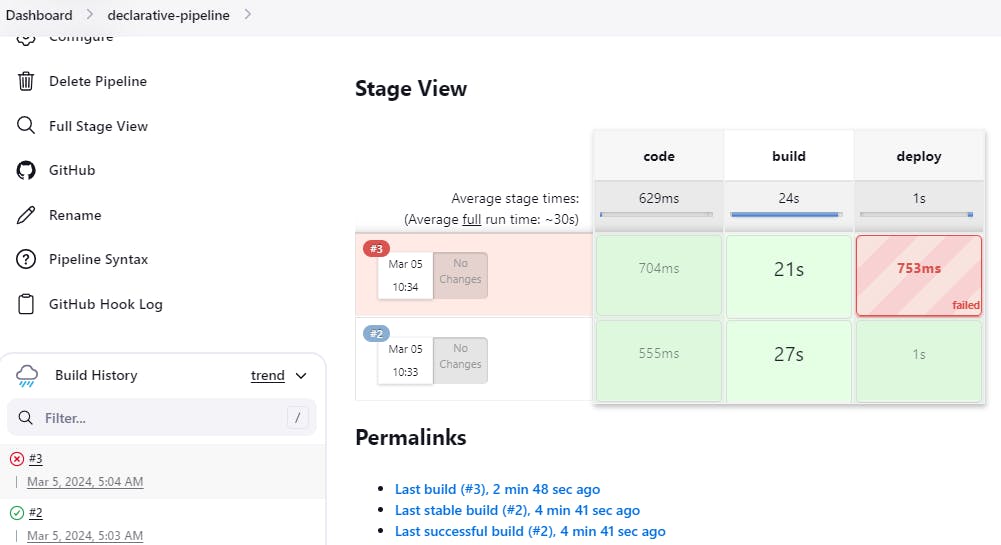
📍You will face errors(port no. 8000 is already allocated) in case of running a job twice, as the docker container will be already created, so for that do task 2.
So, remove/ delete your 1st image using command sudo docker rmi <img-id> --force
📑Task 2: Enhance Pipeline with Docker Groovy Syntax
- Create a docker-integrated Jenkins declarative pipeline using the
dockergroovy syntax inside the stage block.
📍Now you just go back to the configuration of your pipeline job.
📍Modify the Pipeline Script.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage("code") {
steps {
git url: "https://github.com/mandgepratik/node-todo-cicd.git", branch: "master"
echo "code cloned successfully"
}
}
stage("build and test"){
steps{
sh "docker build -t node-app-test-new ."
echo 'Code Build Successfully'
}
}
stage("deploy") {
steps {
sh "docker-compose down && docker-compose up -d"
echo "Node-app deployed successfully"
}
}
}
}
📍Save & Run once again.
📍Congratulations, your pipeline is running successfully.🎊
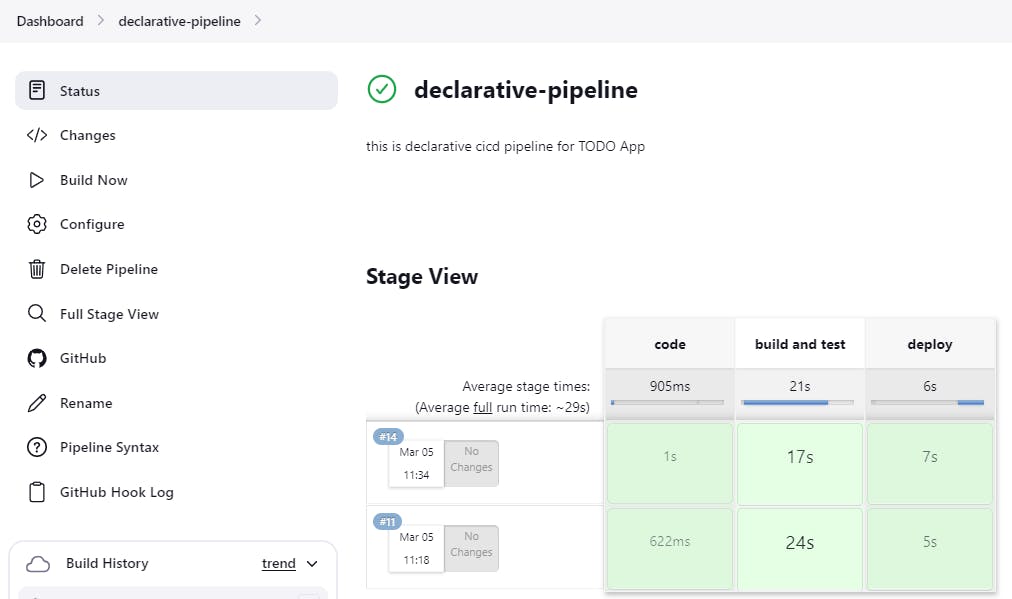
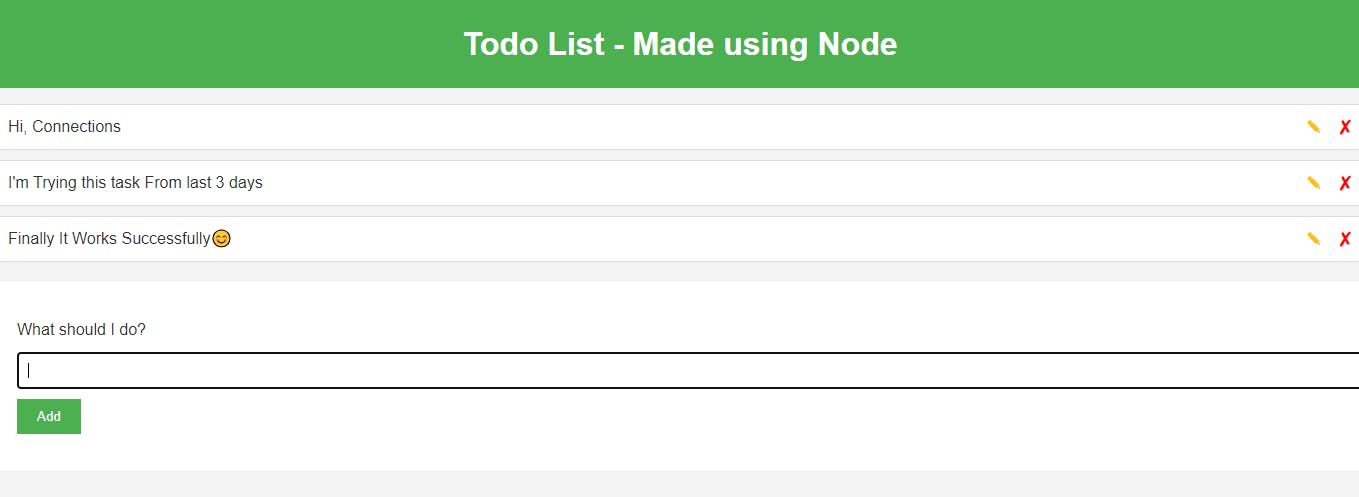
📍Then check your application, use your EC2 public-ip:8000
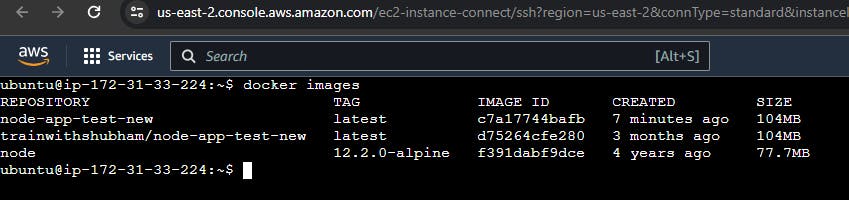
📍You can check on your terminal, You'll get latest image of your repository.
🌌Conclusion
In conclusion, using a declarative CI/CD pipeline with Docker commands in Groovy syntax offers a streamlined and efficient way to automate your build, test, and deployment processes. By defining your pipeline stages and steps within a Jenkinsfile, you can easily manage and version control your CI/CD workflow.
😊 Happy learning!
